ISO 27001 Controls: Best Practices
In a world with dozens of security frameworks and standards to choose from, one of the most well-known and globally recognized is ISO/IEC 27001. Revised in 2022, it updated controls to address emerging risks and modern business practices such as remote working and cloud usage. It provides a structure for protecting critical and sensitive data through the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of an information security management system (ISMS).
The current version of this standard, ISO 27001:2022, is organized around a set of 93 controls outlined in Annex A, which are grouped into four categories:
- Organizational controls: Policies, processes, and practices that establish the overall security governance structure.
- People controls: Measures focusing on personnel, including training and awareness, to ensure that staff understand and fulfill their security roles.
- Physical controls: Protections for physical assets and environments to mitigate risks like unauthorized access.
Technological controls: Safeguards such as encryption, malware protection, and access control systems to defend against digital threats.
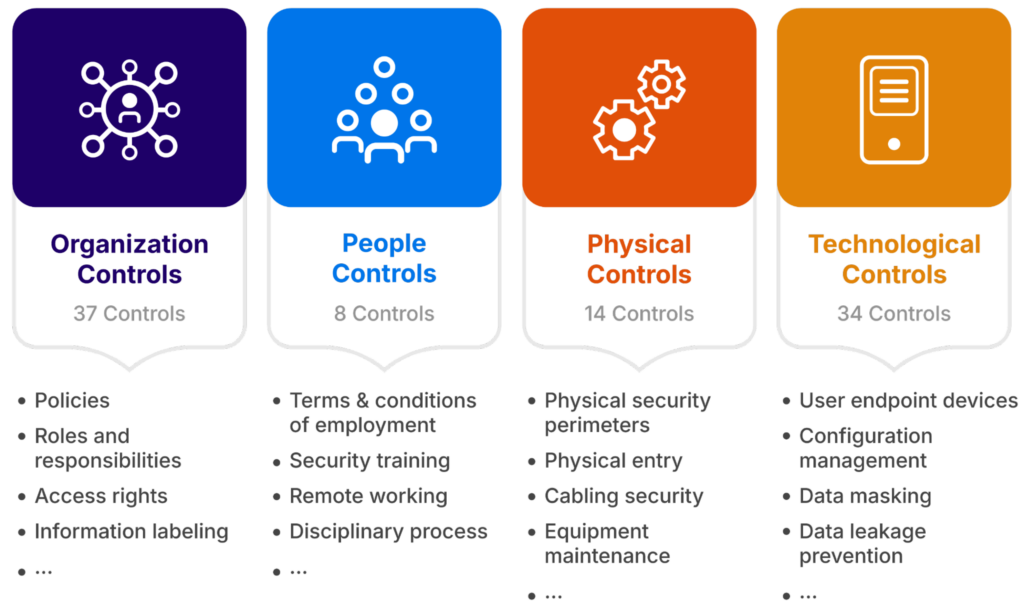
ISO 27001:2022 Control Categories (source)
These control categories mark a change from the prior version of ISO 27001:2013, which broke down the controls across 14 domains:
- Information Security Policies
- Organization of Information Security
- Human Resources Security
- Asset Management
- Access Controls
- Cryptography
- Physical and Environmental Safety
- Operation Security
- Communication Security
- System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance
- Supplier Relationships
- Information Security Incident Management
- Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management
- Compliance
Summary of best practices related to ISO 27001 controls
The importance of ISO 27001 lies in its ability to safeguard critical organizational assets, thereby enhancing customer trust and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. ISO 27001 is a certifiable standard, one that requires organizational commitment at all levels and a dedicated and planned approach to implementation. The table below summarizes the best practices that can smooth the process of implementing the controls found in Annex A of ISO 27001; the sections that follow provide additional detail.
| Best practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Keep a current asset inventory | Maintain a comprehensive inventory of all information assets to support asset management and risk assessment requirements. |
| Use dependency mapping | Map dependencies between systems to understand interconnected risks and enhance continuity planning. |
| Implement configuration control | Track and manage configurations to ensure that all changes are documented and aligned with security requirements. |
| Set up automated change management | Implement workflows to document, review, and approve changes, reducing security risks from unauthorized modifications. |
| Continuously Document processes | Automate documentation updates for audit readiness, ensuring that compliance records are consistently accurate and up-to-date. |
Best practices for implementing ISO 27001:2022
Keep a current asset inventory
Maintaining a comprehensive inventory of information assets is foundational for implementing ISO 27001. An accurate asset inventory means that organizations can identify and classify their assets based on criticality and sensitivity, supporting risk assessment and management. It can also serve as the single source of truth for assets in the organization, reducing misalignment between stakeholders such as asset owners, IT, and security.
Why it matters: An inventory enables organizations to know what they must protect, avoid gaps in coverage, and prioritize controls based on asset value. This also ties directly to the required risk assessment that is performed as part of initiating ISO 27001 at an organization.
Implementation tip: Leverage automated tools to catalog hardware, software, and data assets, ensuring that the inventory is regularly updated and assigning ownership and all necessary data to support asset lifecycle management.
Use dependency mapping
Understanding the interdependencies between systems and services is crucial for effective risk management and continuity planning. Dependency mapping identifies how systems and processes interact, revealing potential cascading failures before an incident while also supporting incident response.
Why it matters: Dependency mapping enhances several processes—such as change management, incident response, and system redundancy—and helps with the design of failover mechanisms by identifying critical dependencies. The ability to see and understand how systems and applications are transmitting data across on-premises and cloud environments is essential to fully grasp data management.
Implementation tip: Use visualization tools to document relationships between systems and applications, incorporating both technical and business perspectives.
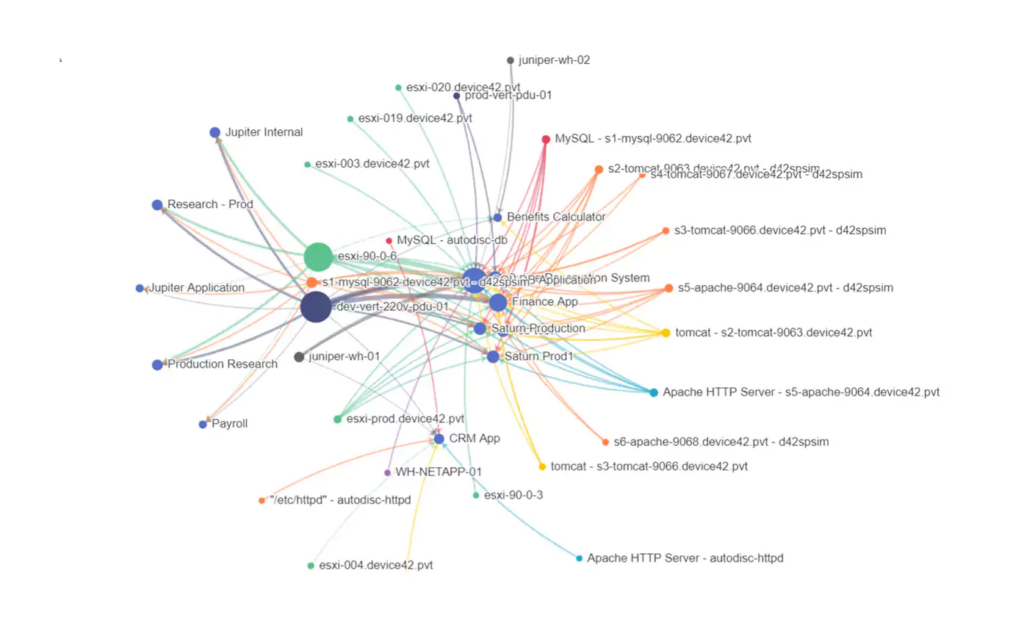
Dependency Mapping (source)
Implement configuration control
Configuration control ensures that system settings are managed in a way that aligns with security policies. This process minimizes vulnerabilities by standardizing configurations and documenting all changes while promoting communication among stakeholders in IT, the business, and security. It also works with an asset inventory to maintain a single source of truth for asset configurations across the organization, including for those operating in the cloud.
Why it matters: Misconfigurations are among the most common causes of security incidents. By controlling configurations, organizations reduce risks tied to human error and unauthorized changes.
Implementation tip: Implement a secure baseline configuration for systems and periodically review compliance. It is also beneficial to promote involvement of key stakeholders early in the process.
Set up automated change management
Change management processes document, review, and approve system modifications, so they do not introduce new risks. One of the most common risks to organizations is unauthorized changes to assets, and automating change management in the organization helps reduce risk while improving efficiency.
Why it matters: Unauthorized or unvetted changes can lead to vulnerabilities and increase organizational risk exposure. Automated workflows preserve transparency and accountability while saving time and resources.
Implementation tip: Integrate change management tools into IT systems to streamline approvals and track changes.
Continuously document processes
Up-to-date documentation is critical for an organization’s security culture and overall approach to governance. It is key for keeping employees, contractors, and customers aware of policies, procedures, and processes and for securing audit readiness and compliance. Automating the creation and updating of compliance records ensures that organizations can demonstrate adherence to ISO 27001 requirements at all times.
Why it matters: Accurate and updated documentation facilitates smoother audits and compliance with policies and procedures and helps identify areas requiring improvement.
Implementation tip: Utilize software that automatically updates policies, procedures, and compliance reports as changes occur in the ISMS. This fosters efficiency, allowing the organization to focus more on enhancements rather than meticulous manual updates.
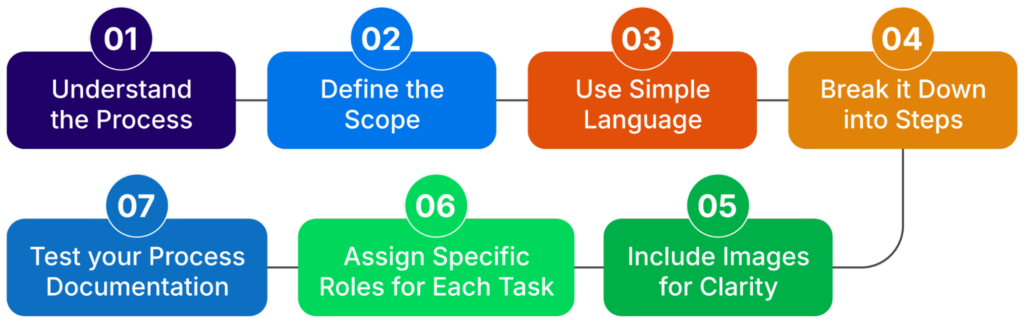
Process Documentation Steps (source)
Aligning best practices to ISO 27001:2022 categories
For the section below, we refine the ISO 27001:2022 controls further into high-level topics within each category and provide corresponding best practices that establish a solid foundation for the implementation of controls. The descriptive implementation details for ISO 27001 Annex A controls can be found in ISO 27002, but we can capture the essence of these controls through their categorization and alignment with common security topics.
Organizational controls
Relevant best practices:
- Keep a current asset inventory
- Use dependency mapping
- Continuously document processes
These controls require organizations to define and document roles, responsibilities, and resources for managing security. Maintaining an asset inventory provides clarity on ownership and accountability of assets, while dependency mapping informs the allocation of resources and relationship between data sets. Continuous documentation is critical for these controls as many of them relate to governance aspects of structure, policies, procedures, and processes.
These controls fall into the following high-level topic areas:
- Governance and oversight
- Asset and information management
- Access and identity management
- Supplier and third-party management
- Incident and continuity management
- Communication and collaboration
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Operational procedures and processes
People controls
Relevant best practice:
- Continuously document processes
People-centric controls emphasize training, awareness, and clear communication, with the addition of a control on remote working to reflect the recent increase globally. Continuous documentation ensures that training materials, records, and employee policies are consistently updated.
These controls fall into the following high-level topic areas:
- Employee lifecycle management
- Information security culture and training
- Work environment and incident reporting
Physical controls
Relevant best practices:
- Keep a current asset inventory
- Implement configuration control
Physical controls, such as access management, benefit from a detailed inventory to track hardware and secure storage areas. Configuration control ensures that security policies extend to physical device settings.
These controls fall into the following high-level topic areas:
- Physical access and facility security
- Physical and environmental threats
- Asset and equipment security
Technological controls
Relevant best practices:
- Keep a current asset inventory
- Use dependency mapping
- Implement configuration control
- Set up automated change management
- Continuously document processes
Technological controls like malware protection and encryption rely on secure configurations and robust change management processes to prevent unauthorized modifications. Additionally, an asset inventory provides a more holistic picture when applying access management, vulnerability management, and logging and monitoring practices.
These controls fall into the following high-level topic areas:
- Access management and authentication
- Vulnerability and threat management
- Resilience and recovery
- Logging and monitoring
- Network and infrastructure security
- Secure development and change management
- Audit and compliance safeguards
Conclusion
ISO 27001:2022 offers a comprehensive framework for managing information security, but its successful implementation depends on the organization’s ability to operationalize its controls effectively and improve upon them. By adopting best practices, organizations can lay a strong foundation for compliance and security.
It is important to remember that ISO 27001 Annex A provides the controls that are required according to the results of your organization’s risk assessment. Once these required controls are identified, it can prove greatly beneficial to supplement the implementation by leveraging ISO 27002, which provides a more detailed blueprint for each control found in Annex A.
The best practices detailed above simplify the implementation of ISO 27001 controls and enhance the organization’s resilience against evolving threats. Whether starting your ISO 27001 journey or seeking to refine your approach, these strategies provide actionable insights for achieving a robust ISMS and strengthening your organization’s security.