Hardware Inventory
Control CapEX and be audit-ready.
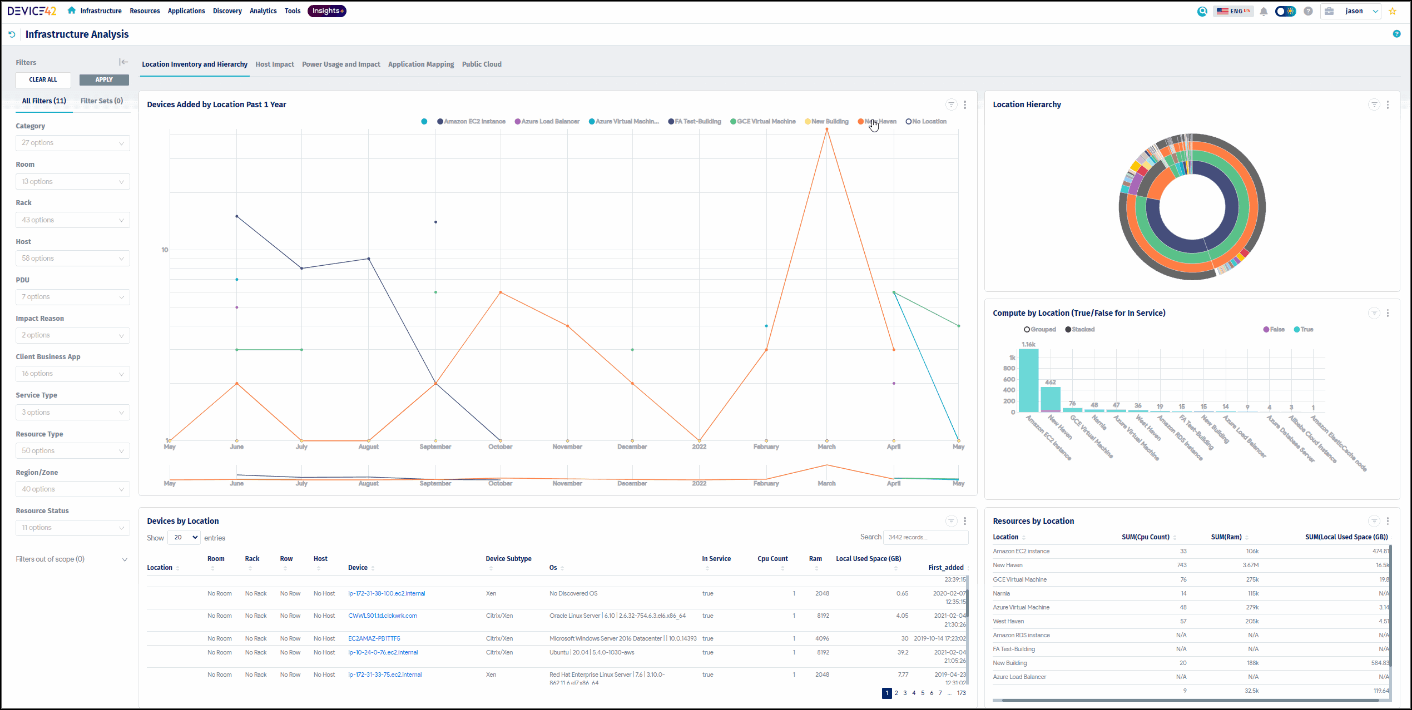
Device42 locates and updates your devices automatically, making it easy to document physical, virtual, blade, clusters, switches or any other device types.
Featuring easy to use, multi-edit, data entry pages, which allow you to add and modify hardware components from a single page. While editing a device, simply open a new tab to see all locations where that part number exists, and inventory counts for that specific model or part number as well.
Track Relationships Between Assets
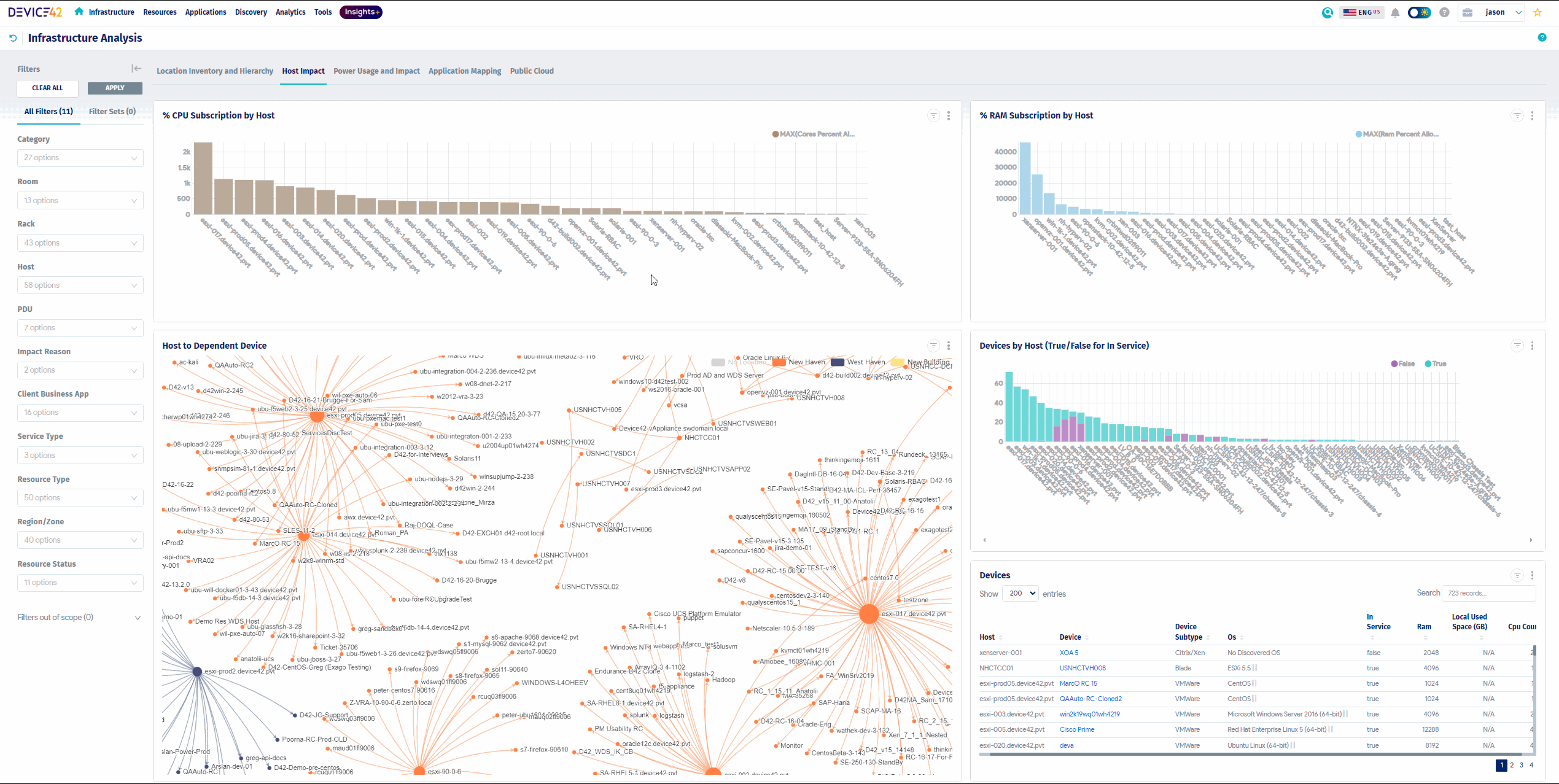
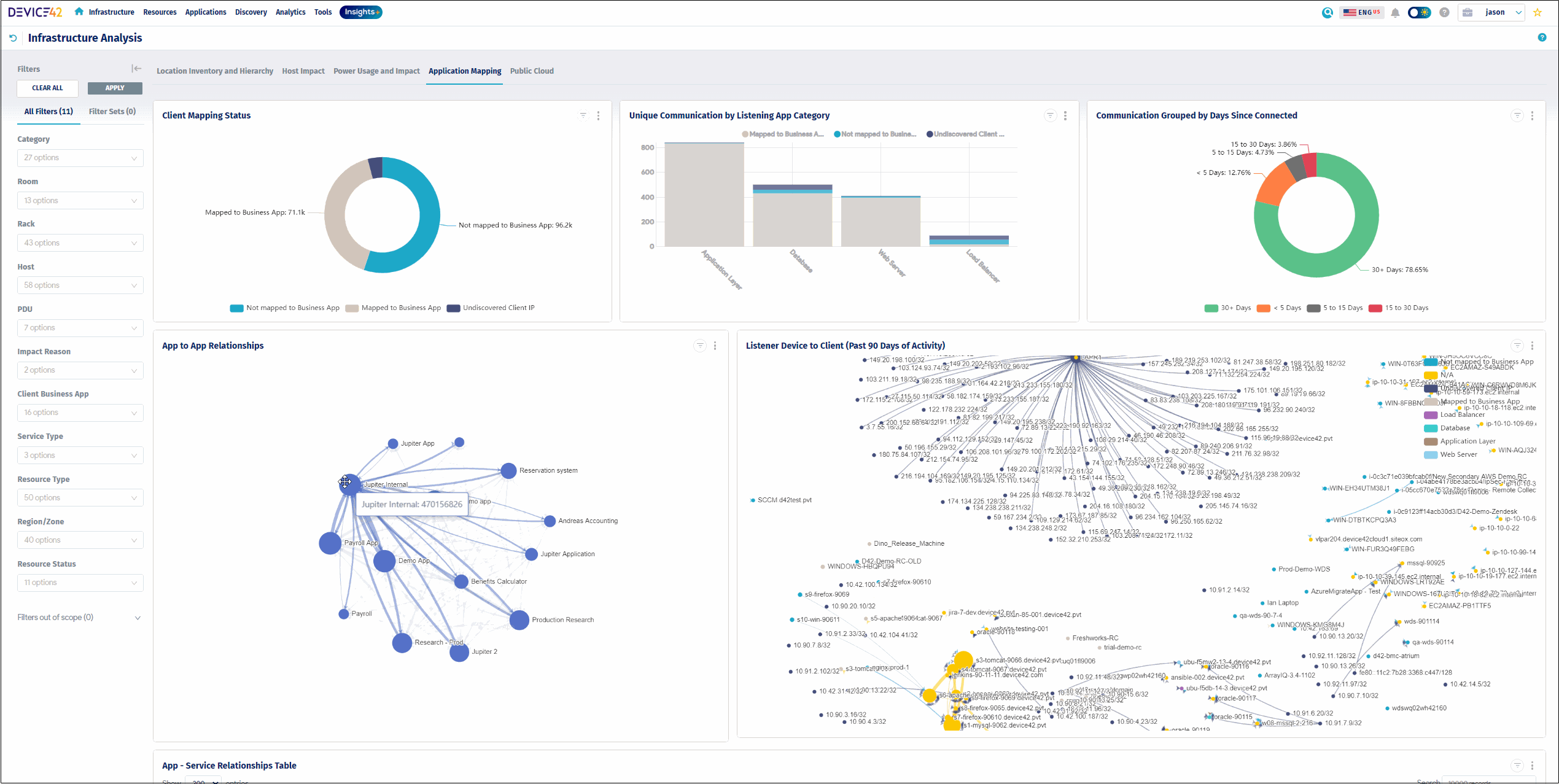
Device42 asset tracking software provides the powerful ability to track and visualize operational dependencies.
Device42’s detailed Impact Charts:
- Display downward dependencies from Virtual Host or Blade Chassis to contained VMs
- Visualize service connections between them
- See a clear map of your operations
- Quickly understand the trickle-down effect of a service interruption if a blade or service were to become unavailable
Virtual Machines, Containers and Cloud Inventory
Effortlessly enumerate data from your physical, virtual, and cloud hosts.
Device42 includes Cloud and server discovery that supports all widely used hypervisors and cloud providers. Built upon native vendor API’s, you can run on-demand or scheduled jobs to reach and grab data from your Hosts and VMs alike, keeping your inventory up to date with new deployments and changes to your virtual and cloud environments, accurately tracking everything from services down to blade layouts to wiring – and more!
Integrate with ITSM Tools
More effectively manage IT service details and quality of response with detailed information provided from Device42 to integrations such as JIRA, Zendesk, and ServiceNow. Leverage Device42 as your single source of truth.
Select Configurations Items and (CIs) to associate them when creating service requests. Sync data such as devices, power units, parts, and racks then search for and navigate to requests that include CIs from Device42. All changes can be viewed through a detailed audit log with a defined source of change and the properties that were updated.

Compliance and Security
Granular and detailed reporting is a powerful tool that provides insight into the daily operations of your IT and infrastructure. Create change history and password reports, and keep all needed parties involved and up to date with device and password expiration audits. Easily maintain an environment focused on security and best practices. Device42 provides an expansive feature set to manage contracts and licensing based upon variables such as user count, licensed CPUs, and whether a given license is perpetual or subscription based.
Go Beyond Just Assets with Our Fully Integrated CMDB
Device42’s CMDB becomes the single source of truth within your organization, which provides a clear view of your IT ecosystem. Identify, manage, and verify all configuration items (CI) in your environment. Track all IT assets and configurations within the company and its services in one place, ensuring configuration records are accurate for greater control over your infrastructure. Unify data and process across teams and across departments, fostering alignment companywide.
Thousands of Customers Across 60+ Countries Trust Device42 for Their IT Asset Management Needs
“Device42 is taking us from anarchy to organization.”
— Ma Iles
Network Systems Manager
International School of Beijing
Ultimate Guide to IT Asset Management
What is IT Asset Management?
IT asset management (ITAM) is a methodology to inventory and manage the quantity, usage, and financial value of IT assets across their lifecycles, associating costs, and risks to each asset to determine their business value. This helps businesses make strategic decisions in regards to purchasing new technology, upgrading existing technologies, contractual obligations, and more.
The purpose of an ITAM strategy is to get a greater financial understanding of the software and hardware the company has in use, the lifecycle of those assets, and the assets the company intends to purchase. Implementing an ITAM strategy helps improve the utilization of current hardware and software and eliminate wasted resources, saving companies time and money.
Types of IT Asset Management
To successfully implement an ITAM strategy, you need to understand what it is and how it functions. There are two main types of IT asset management solutions: software and hardware. Organizations also track physical and location-specific assets such as desks, chairs, vehicles, and buildings, but those usually fall in the facilities asset management space and do not involve IT.
Hardware
Hardware as you might imagine encompasses physical IT assets that support the business including: server cabinets, racks, physical servers, desktop computers, peripherals (keyboards, mice, sound equipment, printers, copiers, routers, and switches). An ITAM strategy for hardware helps you understand what hardware is being used, where it is located, who is responsible for it, and the life cycle to avoid downtime and maximize the financial value of each hardware asset. The Finance team can also use this information for amortization.
Software
Software assets have become increasingly important to track especially for complex software licensing agreements for hypervisors, public cloud, private cloud, containers, virtual machines (VMs), and business software. Understanding the number of software types, licenses, and the amount of virtual resources consumed is critical to understanding the financial implications of software assets. By having an understanding of software utilization, you reduce the number of existing licenses that are not in use and plan appropriately for future needs. Research has shown that on average 37% of enterprise software is waste, where the companies own the software, but it is not being used for anything productive.
How Does ITAM Work?
The main function of ITAM is to account for a company’s assets – deploying, maintaining, upgrading, and deposing them. This helps companies make informed decisions on what future hardware or software they need to purchase and what the lifecycles of those assets will be.
In order to successfully account for assets, companies use IT asset tracking. The way ITAM works is typically there is software that is used to automatically discover, collect, and create an inventory of all the assets.
One risk with that is that some software products may not be able to speak the right language with the assets and not be able to communicate and discover certain resources. Some organizations to this day rely on old-fashioned manual tracking of resources. They literally walk around a data center, office floors, and business centers, and count the number of computers, servers, racks, etc., and put that information into a spreadsheet. The downside of this is that in a dynamic environment like IT, the data quickly becomes obsolete as soon as the spreadsheet is done.
IT Asset Tracking
IT asset tracking refers to the utilization of an IT asset, its location, and if the asset is in service. Good asset tracking software needs to track both hardware and software and take into account specific details such as SKUs, purchase date, cost, technical specifications, and end of life/end of sale (EOL/EOS).
Many years ago, asset tracking was a lot easier than today. When a physical server, switch, or router was connected to the network, it typically stayed there and did not move. With the introduction of virtualization, cloud computing, software-defined networking (SDN), serverless computing, containers, and other technologies that are more dynamic in nature一where they come up to complete a task and are destroyed in minutes or seconds一it becomes more and more difficult to track resources in the same way it was done in the past. Additionally, employees worked in a physical office space and all their equipment were tied to a LAN (local area network).
Today, many organizations allow employees to work from home, making it even harder to track company assets as they move between offices, locations, and even time zones on a regular basis. These moves and changes are impossible to track with the old-fashioned spreadsheets. IT teams now use advanced asset management and tracking software to better understand their entire ecosystem of IT resources.
Inventory Tracking
Unlike IT asset tracking, the goal of inventory tracking is the sale of assets and the quantity needed for replenishment. Inventory tracking is incredibly important for businesses that sell physical assets in order to manage stock to avoid excess or no stock.
IT teams in an inventory tracking business deploy, manage, and leverage more modern technologies such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), QR and barcode scanners, GPS-based trackers, and physical building access data to get a real-time, full picture of their inventories. The IT teams provide these services to the business and must be constantly on the cutting edge in the way they deploy the latest and greatest technology for inventory tracking.
IT Asset Lifecycle
IT asset lifecycle management is the practice of understanding the stages in the life of an asset and the effective planning, purchasing, utilization, and retirement of that asset.
- Planning. Before you place an order, there should be a clear, documented acquisition strategy that includes the requirements and purpose for the assets, including corporate procurement policies, any green initiatives that the equipment must meet, and the equipment brands and models that can be ordered.
- Procurement. You have convinced the CIO to approve a budget for new servers. Now it’s time for Procurement to negotiate the best possible pricing and terms.
- Fulfillment. Once a vendor has been chosen and the contracts signed, the vendor sends you the new servers.
- Deployment. Your new servers have arrived at the dock. Now it’s time to log in the assets and deploy them into service.
- Monitor. During this phase you are capturing performance data to ensure that the servers are optimized for their environment.
- Service. To keep your assets within performance thresholds, service and maintenance will be required. This might include scheduled maintenance, OS updates, and emergency repairs.
- Disposal. After the length of time the business has put forth as part of the lifecycle plan, or when for example the servers’ processors no longer can support a new versions of business applications, it’s time to determine if the asset can be used for other applications, as a backup, or if disposal of the asset is necessary.
IT Inventory Management
IT inventory management refers to the management of all the technological assets that the IT team is responsible for and that the business relies on to function. At any given time, IT teams must know how many of what they have and in what stage of their lifecycle they are. For example, when a new technology or operating system is released that is more secure, cheaper and/or faster, the IT team may decide to “refresh” their older technologies.
For this reason, they must know what they have today, and what requires refreshing. And when they go through the refresh process, they must have processes in place to ensure business continuity throughout the upgrades and updates. Without proper IT inventory knowledge, tasks such as cloud migration, Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) activities, and IT upgrades and updates would be extremely hard and risky.
IT Asset Management Solution Features
There are many IT asset management solutions available, but not all solutions are created equal. Three key capabilities that should be considered with any ITAM solution are: Depth & breadth of automated discovery, dependency mapping, and integrations with other IT operations tools.
ITAM Discovery
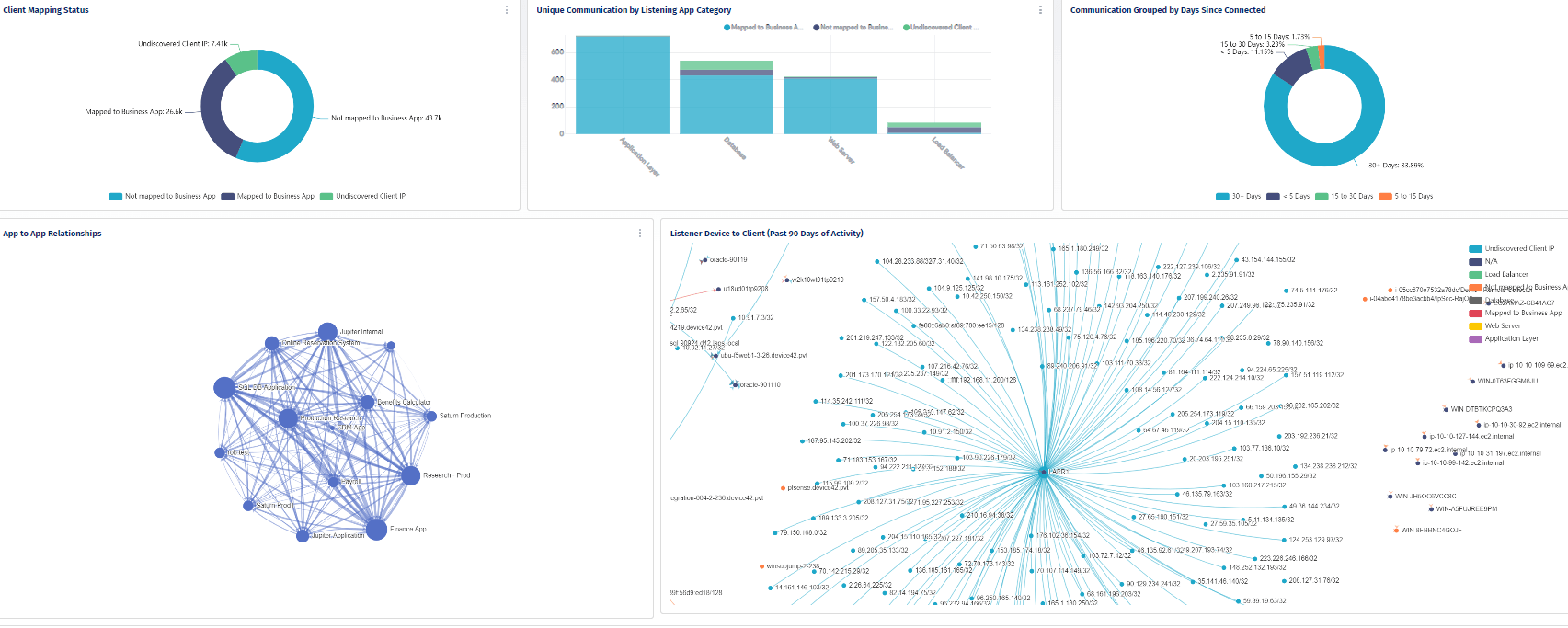
The most important aspect of an ITAM solution is the accuracy of information captured and breadth and depth of technology discovery. The system should be able to discover legacy systems such as mainframe technologies, all the way to the latest cloud containers and technologies. If the ITAM information is incomplete, incorrect, or not up-to-date, you will not have the insights to make accurate decisions. An ITAM solution is the foundation for your decision making and needs to capture all the current assets, who is using them and the frequency, the location of assets, and the estimated life cycle of the assets. To truly understand the impact the asset has on the environment, it’s important to understand the dependencies the assets have with each other.
Application Dependency Mapping
To get a complete picture of the impact and importance an asset has on your business, you need to understand the asset relationships and dependencies on the business functions. For example, you may think that a certain service or software has little to no value on its own, but it may have key functionality that integrates with critical business software. Application dependency mapping provides a visualization of all assets in your ecosystem and how they work together, making it easier to identify the true impact of an asset on your business.
Integrations
An ITAM solution that snaps into and integrates with other current IT operation applications is important to reduce overhead, downtime, manual labor, and human errors. By integrating an ITAM solution with your IT Service Management (ITSM) / ticketing system, you can reduce the amount of time needed to identify IT assets for incident and change management and help the ticket owner gain valuable insights to completing the task. The same information can be leveraged by the Compliance team to quickly pass audits. Migration teams can leverage the information to improve the speed at which they can update and migrate assets. The data can be leveraged with the finance systems for the Finance team to have better visibility into IT costs by business unit.
IT Asset Management Benefits
An ITAM strategy empowers you to manage the financial, inventory, contractual, and risk management responsibilities of the lifecycle of assets.
ITAM Financial Benefits
- For certain CapEx costs, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows for depreciation of assets, which is listed on company tax returns as an expense. If there is no documented, up-to-date inventory of IT assets, your company might be missing out on potential tax savings.
- Make informed purchasing decisions and improve the budgeting process so that you procure only assets that are needed.
- Reduce costs and waste by identifying assets that aren’t being used or can be decommissioned.
- Business uptime can be improved by reducing the amount of time it takes to solve problems that impact the business with quicker access to IT assets.
ITAM Inventory Benefits
- An accurate IT asset inventory integrated with an IT service management (ITSM) solution improves the speed to identify impacted assets when an incident occurs.
- Integration with third-party apps like Freshworks, ServiceNow, and Zendesk can help you streamline your IT maintenance processes.
- Whether you are planning for short- or long-term capacity needs, an up-to-date IT asset inventory gives you the information to determine if you can shift assets to support business needs or require additional resources.
ITAM Contractual Benefits
- For leased IT assets, having easy access to the details of the agreement and the performance of the assets gives you strategic insights for negotiations when it is time for renewals.
- Software audits, especially a Microsoft audit, can be easily documented, provided to the vendor based on licenses in use, and only pay for what you use.
- If you are responsible for customer assets in your environments, an ITAM solution provides the tracking to ensure that you know where the assets are located, scheduled maintenance dates, and criteria to meet contractual obligations.
ITAM Risk Management Benefits
- An accurate IT asset inventory increases support for security and disaster recovery preparedness.
- With an understanding of all your IT assets in your entire estate, you have better control over the IT environment, reducing downtime and risk.
- An ITAM solution effectively tracks and enforces asset policies and regulatory requirements, helping to identify and eliminate risks before they can become actual problems.
IT Asset Management Risks
Lack of Visibility
You can’t manage what you don’t know exists. The first step in IT asset management is to know what assets you have, where they are located, if they are operational, and what risk exists if there is a failure. An ITAM tool with automated discovery can keep your inventory up-to-date and accurate.
No IT Asset Management Strategy
IT asset management best practices recommend that a strategy be implemented to manage the operation, maintenance, and risks associated with ownership of IT assets. To develop an ITAM strategy, there are two necessary steps: (1) Assessment and identification of all assets in your IT ecosystem, and (2) Management and controls established to mitigate risk.
An ITAM tool is a tremendous help to discover all assets connected to your network, but not all ITAM tools are created equally. The heart of an ITAM solution is the discovery functionality. When evaluating an ITAM tool, make sure that the discovery function captures all types of assets in your environment.
An ITAM solution provides an accurate and up-to-date IT asset inventory, but to mitigate any risks, you need to have a strategy for management and controls of the IT assets. You can look to industry standards to build your strategy such as referencing the International Association of Information Technology Asset Managers (IAITAM) Best Practice BluePrint and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 142242 to establish and configure a physical asset hierarchy.
Each area, when not done well, contributes to ineffective IT asset management.
Over or Under Maintenance
During the operational phase of an asset, recommended maintenance is important for optimum performance. Over maintenance of an asset can not only incur unnecessary costs, but it can also increase risk of failure by impacting normal functions. Under maintenance can cause the performance of the asset to degrade over time, increasing the risk of failure. When it comes to maintenance, follow the manufacturer- and industry-recommended maintenance schedules.
Organizations rely on IT Performance Monitoring tools to assess and monitor the health of IT assets such as servers, network devices, bandwidth, and applications and make necessary changes to maintain optimal end user performance experience. Of course, when the performance tools tell the user that there is a problem, ITAM is what helps to identify the location, ownership, and other details of the asset in question to fix the problem quickly.
Improper Operations
IT teams can face serious challenges when assets are not managed appropriately. For example, there might be a virtual server that is throttling in CPU or memory utilization constantly above 90%, and another server is hardly being used. The administrators need to know what type of systems they have, the memory, CPU and storage allocation, and what they can handle.
Performance management tools can help with these situations, but administrators should know in advance what type of technology they need and for what type of business need, and allocate the appropriate resources for the specific type of business needs and function.
IT Asset Management Best Practices
According to the International Association of Information Technology Asset Managers (IAITAM), there are 12 best practices for developing a sound ITAM strategy.
- Program Process. This is the centralization of all IT assets (hardware, software, mobile, and cloud) throughout their lifecycles to support the IT organization.
- Program Management. A well organized ITAM program is necessary and should adhere to IAITAM Best Practice BluePrint, which helps guide organizations through the process of establishing an ITAM strategy.
- Policy Management. Clear and easily understood policies need to be defined and enforced throughout the assets’ lifecycles.
- Communication and Education Management. As part of the ITAM strategy, ongoing communications, education, and training are necessary throughout the IT organization to ensure that the policies and procedures are understood and followed by all stakeholders. This supports change management initiatives throughout the organization.
- Project Management. Strong project management ensures that lifecycle initiatives are undertaken in an organized and effective manner.
- Documentation Management. This is fundamental to your ITAM strategy, but IT asset details such as invoices, software licenses, and certificates need to be maintained for the lifecycle of IT assets.
- Financial Management. The purpose of ITAM is to extract as much value from IT assets as possible. Management of forecasting, procurement, budgeting, chargeback, financial audits, and billing are necessary for an ITAM strategy.
- Compliance and Legislation. One of the benefits of ITAM and an ITAM solution is that it keeps you audit-ready and makes it easier to prepare for an audit.
- Vendor Management. According to IAITAM, you should establish a “documented communication protocol” and “build a library of interactions” as part of your ITAM strategy.
- Acquisition Management. Before you place an order, there should be a clear, documented strategy that includes the requirements for each category of IT assets, including corporate procurement policies, any green initiatives that the equipment must meet, and the equipment brands and models that can be substituted if the model requested is not available.
- Asset Identification. Each IT asset needs to be identified, located, and placed in an asset management tool, such as Device42.
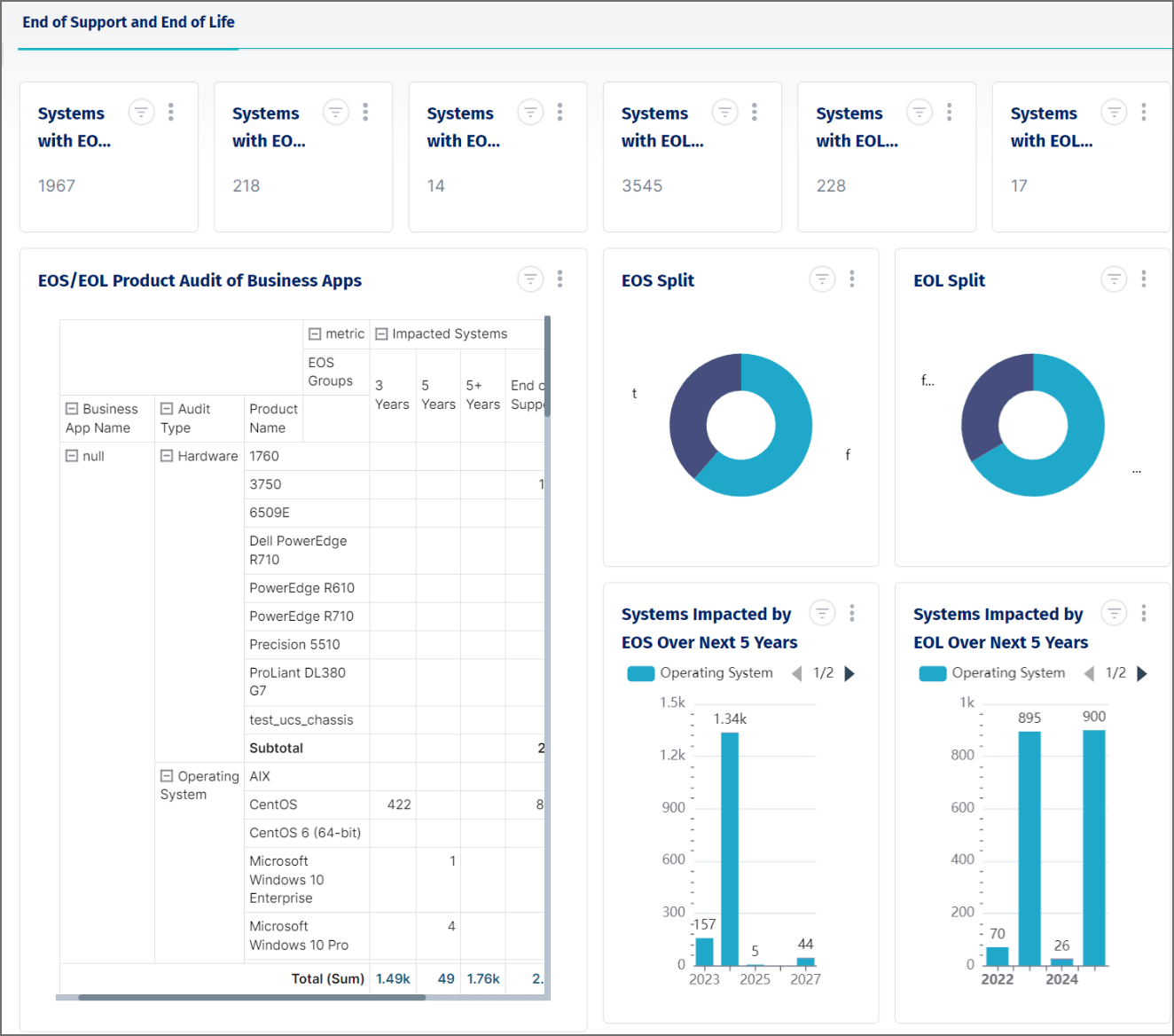
- Disposal Management. A disposal management strategy is important when an IT asset has outlived its usefulness, no longer operates properly, or parts can’t be acquired because the model has been identified as an end-of-sale (EOS) with the manufacturer. This helps obtain any financial value the asset might have, provide an environmentally friendly way to dispose of potential harmful materials, and provide other organizations such as nonprofits with needed equipment.
IT Inventory Management vs. IT Asset Management
You might think that the IT Inventory Management and IT Asset Management are interchangeable, but they have different applications.
ITAM are best practices to track IT assets in the sense of depreciation value, contractual, and inventory functions to support lifecycle management and important IT environment decision making. IT inventory management on the other hand is a business process for managing, storing, counting, and maintaining an inventory of such items. An organization may have IT inventory management, keeping track of things they own, but not have an IT Asset Management solution, which is very specific to the IT assets and their valuation and usage.
The purpose of asset management is to ensure the value and availability of assets to support business goals.
Agent-Based and Agentless Asset Management
IT asset discovery is the heart of an ITAM solution. The discovery tool needs to be able to speak the language of the assets to communicate with in order to discover them and collect data from them. Agentlessly, the discovery solution can communicate using various established protocols, the primary being SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), and others that include WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation), XLM (Extensive Markup Language), SSH (Secure Socket Shell), and more. The more languages the discovery tool can support, the better, as it will discover a wider variety of technologies from the IT environment.
To get even deeper data or data in resources such as desktops that do not have one of the above protocols turned on, then the need of an agent is required. Agents are small applications that run in the background on the systems, where the discovery tool can communicate in its own language and collect the necessary data on those resources.
Agentless Discovery
Agentless discovery uses the target asset’s management protocols and APIs to retrieve data. For TCP/IP network scanning, agentless discovery is the best.
How Agentless Discovery Works
With agentless discovery, the first step is for TCP/IP networks to identify the attached physical or virtual platforms capable of running software.
Agentless scanning uses a central management server to connect to remote operating systems. Once connected, the server runs a scheduled scan to extract raw application information.
The benefits of agentless discovery include:
- No need to install and maintain agents across your environments
- Non-invasive method because authentication is not required
- Requires very minimal implementation time
- No extra cost for installation, maintenance, or upgrades of agents on target resources
Once an agentless discovery scan is completed, a Zero Footprint approach runs a task on discovered devices and machines and periodically sends back an inventory to the ITAM server. The challenge is to get the scheduled task on the machines and devices. Once the scheduling is set up, the benefit of this approach is that scans are always initiated by the ITAM server, making this one of the most secure options.
The downside of agentless discovery includes:
- Requires all devices to be in the network and switched on
- Elevated privileges are needed to execute the scan
Agent-Based Discovery
Agent-based discovery requires an agent on devices and machines. The scan runs periodically and extracts information about the applications.
The benefits of agent-based scanning include:
- Reliability
- Depth of inventory captured
- Ability to scan remote devices that do not alway have access to the network
The downside of agent-based discovery includes:
- Preparation and testing of the agents before deployment
- Deployment and management of agents
- Upgrades / updates to the agents
Both agent-based and agentless IT asset discovery have their advantages and disadvantages. The key is to understand the information needed to be collected and specific goals of your organization to determine the appropriate solution. In most cases, if you have an ITAM solution that supports both agent-based and agentless discovery, that is the most optimal option.
ITAM for ITSM
ITAM and ITSM have different purposes, but they both focus on governance and on ensuring that the IT technology investment is enabling business goals. ITAM is concerned with the entire asset’s lifecycle from procurement to disposal. In relation to ITAM, ITSM is concerned only with the IT assets operational phase to support service delivery. ITSM solutions are the operational backbone of IT teams that manage the assignment, tracking, and resolution of IT tickets.
The importance of IT asset management processes and tools for an IT organization is often viewed as merely providing a laundry list of hardware and software assets that has minimal value to the organization as compared to IT service management (ITSM). However, ITSM platforms that rely on the best source of information coming from ITAM solutions will be that much more valuable, as the ITSM administrators will have access to much more IT information at their fingertips coming directly from the ITSM platform, that can help them solve problems faster and with more correct results. Ultimately, ITAM and ITSM are complementary.
ITAM vs. CMDB
You might think that an IT asset management (ITAM) solution and a configuration management database (CMDB) are interchangeable, but both have distinct purposes.
A CMDB is used to model IT asset relationship information from the service and operational perspective, such as configurations, change risk, and impact analysis. ITAM solutions typically track IT asset information based on costs and financial aspects, such as the lifecycle and inventory of an asset from commission to decommissioning, contracts, vendors, and the financial aspects.
It is possible to use the CMDB for ITAM asset inventory since most CMDBs provide customization features. The problem arises if the CMDB becomes over-populated with IT asset data, leading to the confusion that IT assets and CIs are the same.
CMDB and ITAM have distinct purposes, but they must be integrated to ensure the IT asset data necessary to support CIs is captured in the CMDB to provide a highly reliabile CI data.
Learn more see: The Technical Guide to CMDB Best Practices
IT Asset Management Reporting
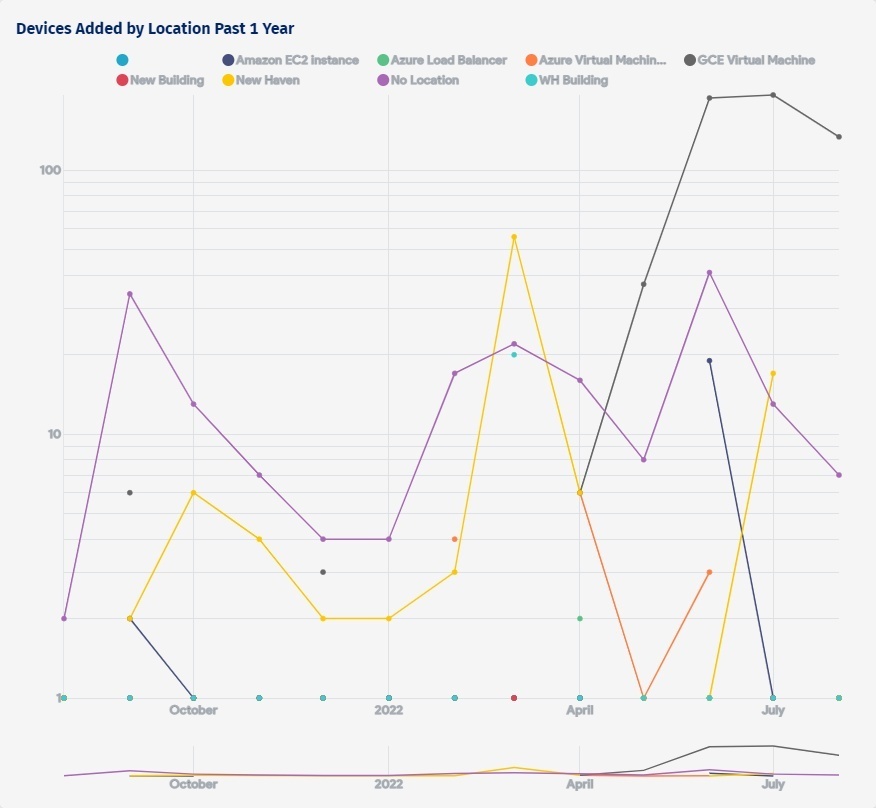
To extract value from the ITAM data collected, an ITAM solution provides reporting and dashboards to help you understand the inventory of your IT assets. You can generate reports on asset types, OS types, vendors一reports can be defined based on any of the data that is collected.
Below are some examples of reports that can help you with daily activities.
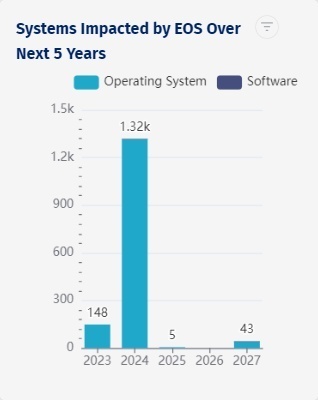
Asset Health Report
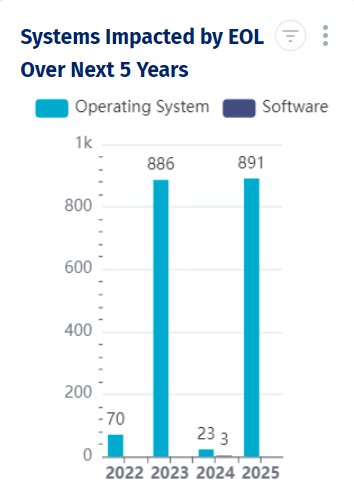
An Asset Health Report gives you insights into incomplete asset profiles, purchase dates to easily identify assets that a vendor has deemed to be at end of service (EOS), unreported incidents to know if a specific asset has had downtime, and ghost assets that are listed as part of inventory, but don’t exist.
Inventory and Procurement Report
The Inventory and Procurement Report details the assets being used and the location, spare parts available, status of orders, vendor details, and depreciation information. The information in the report helps you keep assets in top performance and plan for end of life (EOL).
Maintenance and Scheduling Report
A Maintenance and Scheduling Report helps you get the most value from physical IT assets by tracking the asset lifecycle, including inspection and maintenance dates. This data helps you understand if the asset is achieving the manufacturer’s estimated life expectancy and plan for end-of-life (EOL) assets.
Financial Asset Report
The Financial Asset Report provides information so that auditors can determine each assets’ potential earnings, run costs, and life valuation. It can also help you determine if the assets are achieving manufacturers’ expected output.
Disposal Reports
A Disposal Report provides data about the disposal status, disposal costs, lease agreement termination dates, and repurchase prices for replacement assets.
IT Asset Management Integrations
Integrations with ITSM
ITAM and IT service management (ITSM) are complementary. ITAM provides ITSM data on the financial governance of IT asset costs as well as insight into the performance of the assets that support configuration items. In relation to ITAM, ITSM is concerned with the IT asset’s operational phase to support service needs.
The benefits of integrating an ITAM solution with ITSM include:
- Improved mean-time-to-resolution (MTTR), or the speed at which IT teams can resolve problems, with increased IT visibility coming from ITSM
- Real-time visibility of the assets, based on location, ownership, OS, updates, etc.
- Notification of routine maintenance, software renewals, and IT hardware orders
- Elimination of unplanned downtime and increased efficiency
- Improved utilization of assets for change management
Integrations with CMDBs
A configuration management database (CMDB) and ITAM repository have distinct purposes. An ITAM repository is used to track what you have and where it is located; a CMDB is used track what you have, where it is located, and how it is all connected.
ITAM collects data on all assets in the IT ecosystem; a CMDB collects data only on the assets that support configuration items (CIs).
A proper ITAM solution can feed a CMDB with more accurate and fresh data. Used in conjunction, the CMDB can become a true single source of truth as it will hold not only data from other sources, but also more accurate data from the ITAM solution.
The benefits of integrating an ITAM solution with a CMDB include:
- Data integrity for the CI and ITAM information
- Improved accuracy since the CMDB is not overpopulated with nonessential data
- Avoidance of data duplication by linking the CIs directly to the assets
Factors to Consider When Choosing ITAM Software
When choosing an ITAM solution, there are a few factors that you should consider.
- Automated Discovery Capabilities. Discovery is the key to identifying and maintaining a useful asset inventory. Make sure the Discovery capabilities capture the types of assets in your environment from hardware to software and to the cloud.
- Dependency Mapping & Dashboarding. ITAM solutions that provide additional insights in the form of reporting, dashboards, and dependency maps can save you much time later and help you make more accurate decisions from the vast amount of data discovered.
- Integrations. It is important that the solution offers integrations with other IT operations software that your company uses to gain the value from the information discovered and to avoid duplicate data in multiple systems.
- Time to Value. You should gain immediate value from the ITAM solution once installed.
5. Support. The provider should have a Support team that is engaged with you as a client and responds quickly without needless escalations.